Foreward
OPEC+ announced on Sunday (April 2nd 2023) that it will be cutting production by 1.1 million barrels per day. Saudi Arabia said Sunday it will cut oil production by 500,000 barrels per day from May until the end of 2023.
The ministry described the move as a “precautionary measure” aimed at stabilizing the oil market. The cuts represent less than 5% of Saudi Arabia's average production of 11.5 million barrels per day in 2022.
OPEC+ will reduce Oil production by roughly one million barrels until the end of the year 2023. But what does that mean in actuality? How does this abstract decision play out? How does that effect you? Are the solutions?
Consider this a primer on everything you wanted to know about oil & petroleum. From extraction, refining, to shipping and how that all plays out on the global stage.
Oil Extraction Demystified
Finding oil requires the use of geologists and underground systemic equipment. (think ground sonar) There are several methods of extracting oil once it is found, the method of extraction depends on how the reserve is found.
Mining: Mining extraction refers to the extraction of oil from tar sands.
Drilling: Refers to simple process of drilling into a reserve or deposit and pumping it to the surface.
Fracking: Hydraulic fracturing or fracking is a process by blasting small fissures into the porous coal bed and then pumping a fluid mixture into it to expand the fissures. There by releasing the oil or liquid natural gas and pumping that to the surface.
The majority of the World’s oil reserves require drilling or fracking to extract. Both of which require pump-jacks to pump the oil to the surface. There are few tar sands and they operate akin to open pit mines.
Once found and brought to the surface, there is quite often a refinery near by for efficiency.
Sweet vs Sour
When people refer to a crudes “sweetness” they are referring to the sulphur content on the crude oil. The more sulphur in the crude, the more inefficient it is at producing yields when it goes through extraction. Thus “Sour Crude” has a high sulphur content, while “sweet crude” has a low sulphur content.
Light vs Heavy
The terms light vs heavy when referring to oil refer to it’s density in comparison to water. The term is used due to transportation cost, due to weight.
Thus light is more desirable to heavy crude due to cost and efficiency of shipping and refinement.
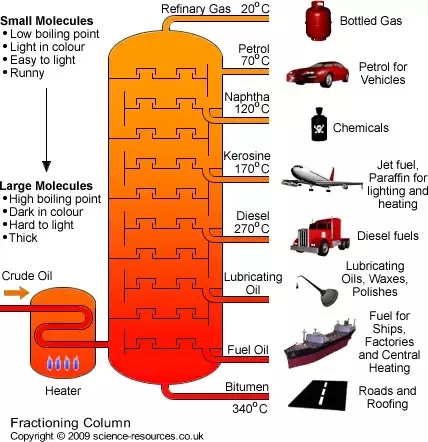
Oil Refinement
In everyday conversation, oil is a catch-all term. There are several different types of “Oil”:
Crude Oil
Bitumen (tar)
Motor oil
Jet fuel
Gasoline
Diesel
Most of these types come from the refinement of crude oil. A process known as fractioning. The crude oil is vaporized and collected as it cools, settling into various sections due to its weight (impurity & carbon levels). A fractioning column diagram is shown below for better understanding.
The varying components are syphoned off, stored into tanks and shipped where needed. All individually traded and used for manufacturing such as plastics. In short oil is the backbone of the modern economy. However, most are so far removed from this that they are oblivious to this fact.
Octane?
Octane rating is an index of a fuel's ability to resist engine knock in engines having different compression ratios. In layman’s terms Octane ratings are measures of fuel stability. The higher an octane number, the more stable the fuel.